English | 中文
Translate JSON datasets precisely while keeping the schema intact
JsonTranslate translates JSON safely and fast — it only touches string values and never breaks your schema. It works with popular translation APIs (Google/Azure/DeepL) and modern LLMs (DeepSeek, OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Siliconflow, Groq, or your Custom LLM). Use it to localize apps, sites, and datasets with global, JSONPath‑targeted, key‑based, or i18n aggregation modes.
Demo: https://tools.newzone.top/en/json-translate
- Features
- Translation Modes
- Quick Start
- Usage
- Notes & Limitations
- Deployment
- Contributing
- License
- Multiple providers (traditional): Google Translate, Azure, DeepL(X)
- LLM providers: DeepSeek, OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Siliconflow, Groq, and configurable Custom LLM
- Preserve JSON shape: translate only string values, keep schema and order
- Flexible scopes:
- Global translation for entire JSON
- JSONPath-based targeted nodes
- Specific key names (simple and mapped modes)
- Selective translation from a start node
- i18n mode that aggregates languages under the same structure
- Mapped translation: write results to different output keys without overwriting originals
- Skip existing i18n fields to avoid accidental overwrites
- Support multiple target languages in one pass
- Works with large files using concurrency and retries
- Dark mode and multi-locale UI
This mode recursively traverses the entire JSON structure and translates all string-type values while preserving the original JSON hierarchy and structure.
Best for:
- Translating all textual content in a full JSON file
- One-click translation without complex configurations
Use JSONPath expressions to precisely locate one or more nodes and translate only the string values within them. Multiple paths can be separated by commas.
Best for:
- Translating only specific sections in a well-structured JSON dataset
- Improving efficiency by narrowing the translation scope in large files
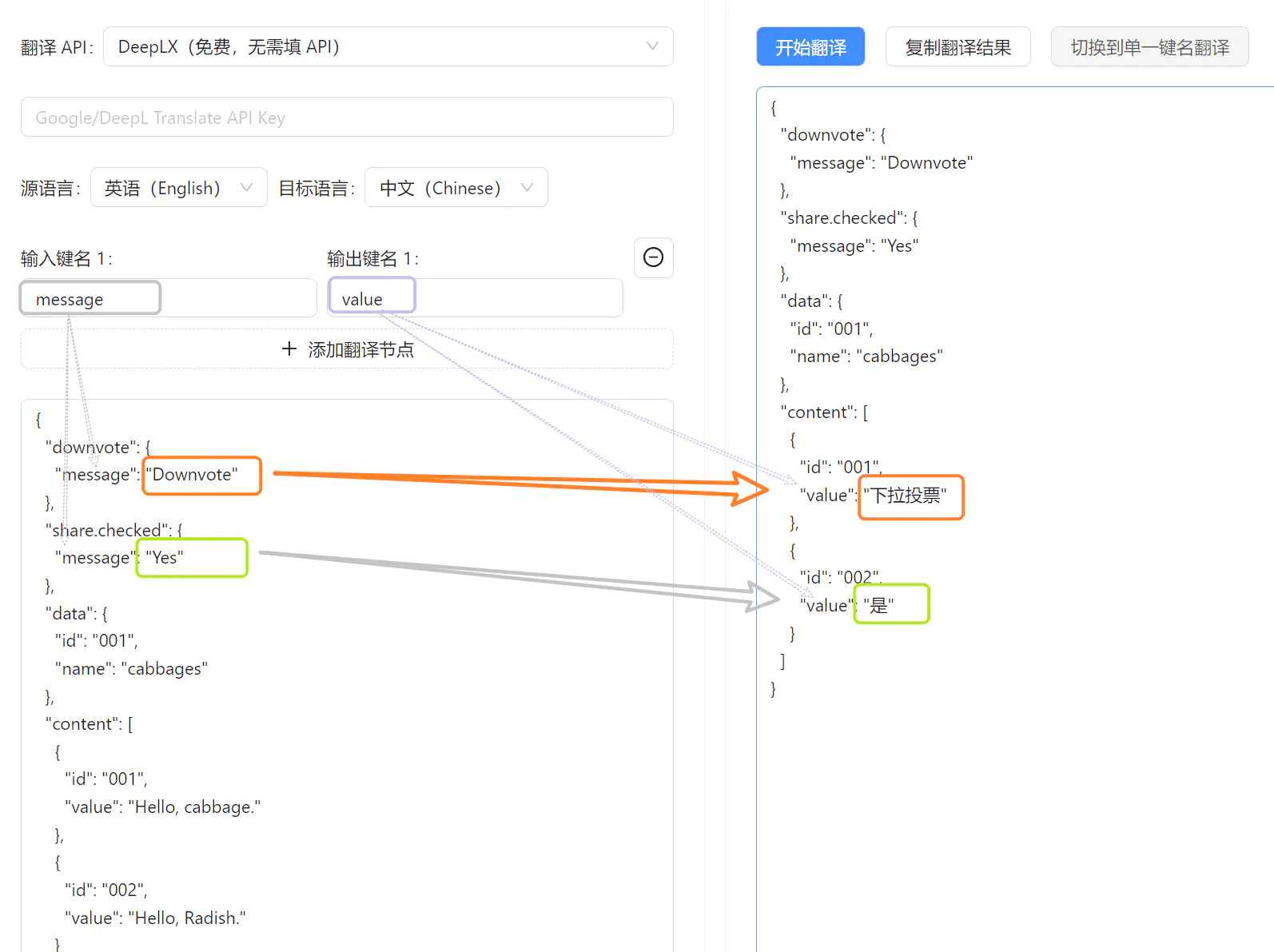
In this mode, you can specify particular key names for translation. Two input options are supported:
- Simple Mode: Enter key names separated by commas (English or Chinese), and the corresponding values will be translated.
- Advanced Mode: Use a key mapping component to define input-output key pairs. Translations are written to new keys, preserving the original fields.
Best for:
- Translating specific fields like
titleordescription - Keeping original data intact by outputting translations to separate keys
Notes:
- Keys are case-sensitive
- The number of input and output keys must match; nonexistent keys are ignored. At least one valid mapping is required
- Pure numeric keys may conflict with array indices (mitigated, but still not recommended)
- Keys containing dots (.) are interpreted as nested paths; avoid dots in key names
Ideal for flat JSON structures, this mode lets you specify a starting node and target field names. The system will search from the starting point and translate all matching fields in nested objects.
Configuration Options:
- Start Key (optional): Indicates where to begin the search—useful when key order matters
- Fields to Translate: Specify target field names; separate multiple fields with commas
Best for:
- Translating fields like
"message"in flattened data structures such as logs or error reports - Simple JSON files with recurring field names requiring partial translation
Designed specifically for multilingual scenarios, this mode aggregates translations under the same field structure, making it ideal for managing multilingual content for websites or apps.
How it works
- The selected source language becomes the source field (e.g.,
zhas the source language means the source field iszh). If set toauto, the default source isen. - It scans all objects containing the source field and adds new fields for each target language at the same level.
- If a target language field already exists, it is skipped to avoid overwriting.
- When both i18n and multi-language modes are enabled, the system creates a unified JSON structure with the source and all target languages—perfect for internationalized projects.
Example
If the target languages are zh and fr, the translated result would be:
{
"title": {
"en": "Settings",
"zh": "设置",
"fr": "Paramètres"
}
}When using the Specific Keys mode, you can switch between single-key and mapped translation in the results panel. Single-key uses the same node as input/output. Mapped translation writes results to different nodes (e.g., A → B, C → D).
JSON stores data in key-value pairs. Keys uniquely identify elements and are used for precise targeting.
Examples explained:
downvote.message: nested key.downvoteis a top-level object,messageis inside it提示词.message:提示词is an object containing amessagekeyshare.owner: this key contains a dot but is one literal key name, not a nested path. Usingshare.owner.namewould be incorrect ifshare.owneris a single key
{
"downvote": {
"message": "Downvote"
},
"提示词": {
"message": "prompt"
},
"share.owner": {
"name": "rabbit"
},
"data": {
"title": {
"id": "001",
"name": "cabbages"
}
},
"content": [
{
"id": "001",
"value": "Hello, cabbage."
},
{
"id": "002",
"value": "Hello, Radish."
}
]
}Note: Keys containing dots (.) are not supported because JSONPath treats dots as delimiters, which can be misinterpreted as nested paths. Prefer keys without dots.
Requirements:
- Node.js >= 18.18
- Yarn 1.x
# Install dependencies
yarn
# Start in dev mode
yarn dev
# Build and run
yarn build && npx serve@latest out
# Build for a single language
yarn build:lang en
yarn build:lang zh
yarn build:lang zh-hantOpen http://localhost:3000 and start translating. You can edit the landing page at src/app/[locale]/page.tsx; changes hot-reload in dev.
Contributions are welcome! Feel free to open issues and pull requests.
Suggested steps:
- Fork the repo and create a feature branch
- Run
yarnandyarn devlocally - Add tests/docs when applicable
- Submit a PR with a clear description
MIT © 2025 rockbenben. See LICENSE.


{ "title": { "en": "Settings" } }