Important
We are actively rewriting this extension to provide a more native and robust experience, similar to what you may be used to when using Jupyter in VS Code. In the meantime, if you have issues with this extension, we recommend you run marimo from the terminal. See our docs to get started.

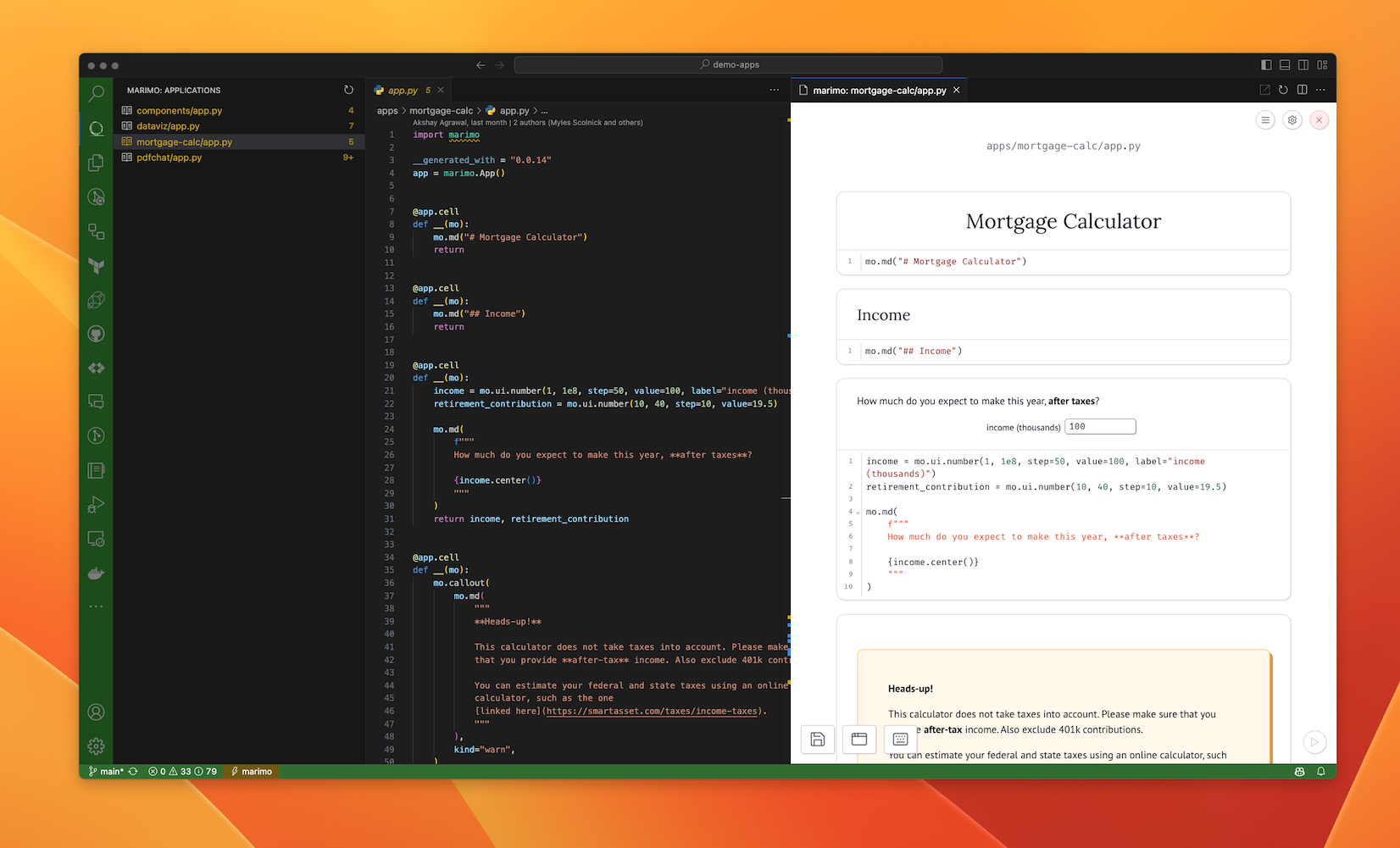
Run marimo, directly from VS Code.
Note
This extension requires marimo to be installed on your system: pip install marimo.
See the installation guide for more details.
Check out the marimo documentation at https://docs.marimo.io/.
- 🚀 Launch marimo from VS Code, in both "edit mode" and "run mode".
- 💻 View the terminal output of marimo directly in VS Code.
- 🌐 View the marimo browser window directly in VS Code or in your default browser.
- 📥 Export notebooks as: html, markdown, or scripts.
- 📓 Convert Jupyter notebooks to marimo notebooks.
- 🧪 [experimental] Run marimo in VSCode's native notebook
VS Code's embedded browser does not support all native browser features. If you encounter any issues, try opening marimo in your default browser instead. For example, the embedded browser will not support PDF render, audio recording, video recording, and some copy/paste operations.
This extension includes an experimental feature to run marimo in VSCode's native notebook interface. This feature lets you use VSCode editors and extensions for writing code while the outputs and visualizations are rendered in a view-only marimo editor. This marimo editor displays outputs, console logs, and UI elements to interact with.
This feature is experimental and may have some limitations. Some known limitations are:
- VSCode automatically includes "Run above" and "Run below" buttons in the notebook toolbar. While these work, they do not make sense with a reactive notebook.
- Notebooks can still be edited even though there may not be an active marimo server. This can be confusing since saving or running will not work.
- For autocomplete to work when using native VSCode notebooks for many packages (including
marimo,numpy, and more) you may be required to include apyproject.tomlfile at the root of the workspace. marimo's editor gets around this by default but unfortunately, the VSCode's native notebook does not. - You cannot access many marimo features in the native notebook (and need to use the marimo browser), such as the variable explorer, dependency viewer, grid mode (plus other layouts), and more - so we show the notebook in "Kiosk Mode" which is a read-only view of the outputs and helper panels.
- VSCode's native notebook does not support different string quoting styles (e.g.
r""",""",f""", etc.), so we default all markdown cells to user""".
To ensure marimo works correctly with your Python environment, you have several options:
Tip
The extension will use the Python interpreter from the Python extension by default. Make sure you have the Python extension installed and configured.
-
Workspace Settings (Recommended) Create or edit
.vscode/settings.jsonin your workspace. You can set the default Python interpreter for your entire workspace, or just for marimo.For setting the workspace Python interpreter, you can set:
{ "python.defaultInterpreterPath": "${workspaceFolder}/.venv/bin/python" }For setting the Python interpreter only for marimo, you can set:
{ "marimo.pythonPath": "${workspaceFolder}/.venv/bin/python" }If you set
marimo.pythonPath, the extension will use that interpreter with-m marimoto invoke marimo. -
Global Settings You can also configure these settings globally in VS Code's settings:
- Set
python.defaultInterpreterPathto your preferred Python interpreter - Verify that marimo is available in your Python interpreter:
/value/of/defaultInterpreterPath -m marimo - (Likely not needed) Set
marimo.marimoPathto the path of your marimo installation. When set, the extension will use this path directly/path/to/marimoinstead ofpython -m marimo.
- Set
-
Virtual Environments If using a virtual environment:
- Create and activate your virtual environment
- Install marimo:
pip install marimo - VS Code should automatically detect the Python interpreter
-
uv projects and package environment sandboxes If you are using
uvto manage your Python project (e.g. with apyproject.tomlfile). You can runuv add marimoto install marimo in your project's environment. Then update your settings to use:{ "marimo.marimoPath": "uv run marimo", "marimo.sandbox": true // optional } -
uvx and package environment sandboxes If you are not creating Python projects and don't want to create virtual environments, you can use
uvxwithmarimo edit --sandboxto run marimo in a sandbox.{ "marimo.marimoPath": "uvx marimo", "marimo.sandbox": true } -
windows If you are on windows, you may have something that looks like this:
{ "marimo.marimoPath": ".venv/Scripts/marimo.exe", "marimo.pythonPath": ".venv/Scripts/python.exe" }
marimo.browserType: Browser to open marimo app (systemorembedded, default:embedded)marimo.port: Default port for marimo server (default:2818)marimo.sandbox: Always start marimo in a sandbox, e.g.marimo edit --sandbox(default:false). Requiresuvto be installed.marimo.watch: Always start marimo with the--watchflag (default:true).marimo.host: Hostname for marimo server (default:localhost)marimo.https: Enable HTTPS for marimo server (default:false)marimo.enableToken: Enable token authentication (default:false)marimo.tokenPassword: Token password (default: empty)marimo.showTerminal: Open the terminal when the server starts (default:true)marimo.debug: Enable debug logging (default:false)marimo.pythonPath: Path to python interpreter (default: the one from python extension). Will be used with/path/to/python -m marimoto invoke marimo.marimo.marimoPath: Path to a marimo executable (default: None). This will override use of thepythonPathsetting, and instead invoke commands like/path/to/marimo editinstead ofpython -m marimo edit.
If you encounter issues, you can open the marimo extension logs by running the marimo: Show marimo diagnostics command from the command palette.
You can also hover over the marimo status bar item in the bottom left of the VSCode window to see the status of the marimo extension.