Build AI-powered robots that see, move, and manipulate objects — in a few lines of code.
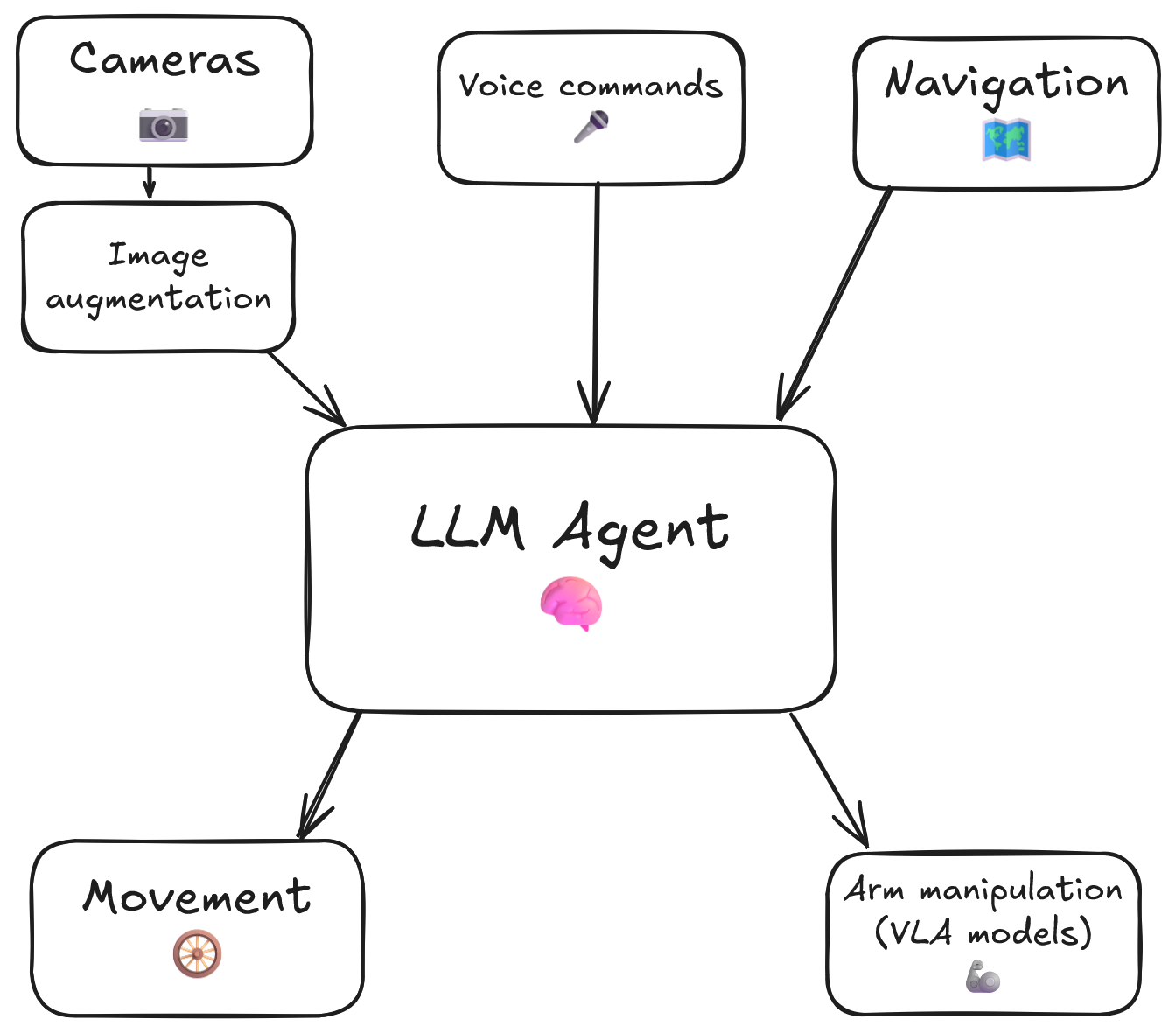
RoboCrew makes it stupidly simple to create LLM agents for physical robots. Think of it like building agents with CrewAI or AutoGen, except your agents live in the real world with cameras, microphones, wheels, and arms.
- 🚗 Movement - Pre-built wheel controls for mobile robots
- 🦾 Manipulation - VLA models as tools for arms control
- 👁️ Vision - Camera feed with automatic angle grid overlay for spatial understanding
- 🎤 Voice - Wake-word activated voice commands and TTS responses
- 🗺️ LiDAR - Top-down mapping with LiDAR sensor
- 🧠 Intelligence - LLM agent control provides complete autonomy and decision making
- 📚 Memory - Long-term memory to remember environment details
The RoboCrew Intelligence Loop:
- 👂 Input - Voice commands, text tasks, or autonomous operation
- 🧠 LLM Processing - Gemini analyzes the task and environment
- 🛠️ Tool Selection - AI chooses appropriate tools (move, turn, grab the apple, etc.)
- 🤖 Robot Actions - Wheels and arms execute commands
- 📹 Visual Feedback - Cameras capture results with augmented overlay
- 🔄 Adaptive Loop - LLM evaluates results and adjusts strategy
This closed-loop system creates AI agents that perceive → reason → act, but in the physical world!
- ✅ XLeRobot - Full support for all features
- ✅ LeKiwi - Use XLeRobot code (compatible platform)
- 🔜 More robot platforms coming soon! Request your platform →
pip install robocrewfrom robocrew.core.camera import RobotCamera
from robocrew.core.LLMAgent import LLMAgent
from robocrew.robots.XLeRobot.tools import create_move_forward, create_turn_right, create_turn_left
from robocrew.robots.XLeRobot.servo_controls import ServoControler
# 📷 Set up main camera
main_camera = RobotCamera("/dev/camera_center") # camera usb port Eg: /dev/video0
# 🎛️ Set up servo controller
right_arm_wheel_usb = "/dev/arm_right" # provide your right arm usb port. Eg: /dev/ttyACM1
servo_controler = ServoControler(right_arm_wheel_usb=right_arm_wheel_usb)
# 🛠️ Set up tools
move_forward = create_move_forward(servo_controler)
turn_left = create_turn_left(servo_controler)
turn_right = create_turn_right(servo_controler)
# 🤖 Initialize agent
agent = LLMAgent(
model="google_genai:gemini-3-flash-preview",
tools=[move_forward, turn_left, turn_right],
main_camera=main_camera,
servo_controler=servo_controler,
)
# 🎯 Give it a task and go!
agent.task = "Approach a human."
agent.go()Add a microphone and speaker to give your robot voice commands and enable it to speak back to you:
agent = LLMAgent(
model="google_genai:gemini-3-flash-preview",
tools=[move_forward, turn_left, turn_right],
main_camera=main_camera,
servo_controler=servo_controler,
sounddevice_index=2, # 🎙️ provide your microphone device index
tts=True, # 🔊 enable text-to-speech (robot can speak)
)Then install Portaudio and Pyaudio for audio support:
sudo apt install portaudio19-dev
pip install pyaudio
pip install audioop-ltsNow just say something like "Hey robot, bring me a beer." — the robot listens continuously and when it hears the wakeword "robot" anywhere in your command, it'll use the entire phrase as its new task.
📖 Full example: examples/2_xlerobot_listening_and_speaking.py
Let's make our robot manipulate with its arms!
First, you need to pretrain your own policy for it - reference here.
After you have your policy, run the policy server in a separate terminal. Let's create a tool for the agent to enable it to use a VLA policy:
from robocrew.robots.XLeRobot.tools import create_vla_single_arm_manipulation
# 🎯 Create a specialized manipulation tool
pick_up_notebook = create_vla_single_arm_manipulation(
tool_name="Grab_a_notebook",
tool_description="Manipulation tool to grab a notebook from the table and put it to your basket.",
task_prompt="Grab a notebook.",
server_address="0.0.0.0:8080",
policy_name="Grigorij/act_right-arm-grab-notebook-2",
policy_type="act",
arm_port=right_arm_wheel_usb,
servo_controler=servo_controler,
camera_config={
"main": {"index_or_path": "/dev/camera_center"},
"right_arm": {"index_or_path": "/dev/camera_right"}
},
main_camera_object=main_camera,
policy_device="cpu",
)📖 Full example: examples/3_xlerobot_arm_manipulation.py
To ensure your robot's components (cameras, arms, etc.) are always mapped to the same device paths, run the following script to generate udev rules:
robocrew-setup-usb-modulesThis script will guide you through connecting each component one by one and will create the necessary udev rules to maintain consistent device naming.
After running the script, you can check the generated rules at /etc/udev/rules.d/99-robocrew.rules, or check the symlinks:
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ ls -l /dev/arm*
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Dec 2 11:40 /dev/arm_left -> ttyACM4
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Dec 2 11:40 /dev/arm_right -> ttyACM2
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ ls -l /dev/cam*
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 6 Dec 2 11:40 /dev/camera_center -> video0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 6 Dec 2 11:40 /dev/camera_right -> video2For detailed documentation, tutorials, and API references, visit our official documentation.
- 💭 Join our Discord - Get help, share projects, discuss features
- 📖 Read the Docs - Comprehensive guides and API reference
- 🐛 Report Issues - Found a bug? Let us know!
- ⭐ Star on GitHub - Show your support!
Built with ❤️ for the robotics and AI community. Special thanks to all contributors and early adopters!