diff --git a/docs/SUMMARY.md b/docs/SUMMARY.md
index 2bcc3ca216..9f151b170d 100644
--- a/docs/SUMMARY.md
+++ b/docs/SUMMARY.md
@@ -68,7 +68,8 @@
* [App Details](user-guide/creating-application/app-details.md)
* [Debugging Deployment And Monitoring](user-guide/debugging-deployment-and-monitoring.md)
* [Application Metrics](user-guide/creating-application/app-metrics.md)
- * [Overview](user-guide/creating-application/overview.md)
+ * [Overview](user-guide/creating-application/overview.md)
+* [Resource Browser](user-guide/resource-browser.md)
* [Charts](user-guide/deploy-chart/README.md)
* [Charts Overview](user-guide/deploy-chart/overview-of-charts.md)
* [Deploy & Observe](user-guide/deploy-chart/deployment-of-charts.md)
@@ -77,6 +78,7 @@
* [Deploying MongoDB Helm Chart](user-guide/deploy-chart/examples/deploying-mongodb-helm-chart.md)
* [Chart Group](user-guide/deploy-chart/chart-group.md)
* [Security](user-guide/security-features.md)
+* [Clusters](user-guide/clusters.md)
* [Bulk Edit](user-guide/bulk-update.md)
* [Integrations](user-guide/integrations/README.md)
* [Build and Deploy (CI/CD)](user-guide/integrations/build-and-deploy-ci-cd.md)
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/clusters.md b/docs/user-guide/clusters.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4cda21c907
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/user-guide/clusters.md
@@ -0,0 +1,210 @@
+# Clusters
+
+Devtron allows you to manage your Kubernetes cluster by:
+ * Browsing information of cluster and its resources.
+ * Managing the added resources to meet the requirements for high speed and storage capacity.
+ * Managing Cluster resources with Kubernetes requests and limits and also individual containers.
+ * Debugging a pod or node by connecting to a terminal.
+
+On the left navigation of Devtron, select `Clusters`. You will find the list of clusters in this section which you have added under [Global Configurations > Clusters & Environments](https://docs.devtron.ai/global-configurations/cluster-and-environments).
+
+You can also search the cluster in the `Search Clusters` bar.
+
+
+
+
+| Fields | Description |
+| --- | --- |
+| **Cluster** | User-defined name for the cluster in Devtron. E.g. `default-cluster` |
+| **Connection Status** | Status of the cluster. The status can be either `Successful` or `Failed`. |
+| **Nodes** | Shows the number of nodes in a cluster. |
+| **Node Errors** | Shows the error in nodes. |
+| **K8s Version** | Shows the version of Kubernetes cluster. |
+| **CPU Capacity** | Shows the CPU capacity in your cluster in milicore. E.g., 8000m where 1000 milicore equals to 1 core. |
+| **Memory Capacity** | Shows the memory capacity in your cluster in mebibytes. |
+
+To see the details of resource allocation and usage of the cluster, click the particular cluster.
+
+## Resources
+
+On the `Resource allocation and usage`, you can see the details of compute resources or resources.
+
+* CPU resources
+* Memory resources
+
+If you specify a `request` and `limits` in the container resource manifest file, then the respective values will appear on the `Resource allocation and usage` section.
+
+
+
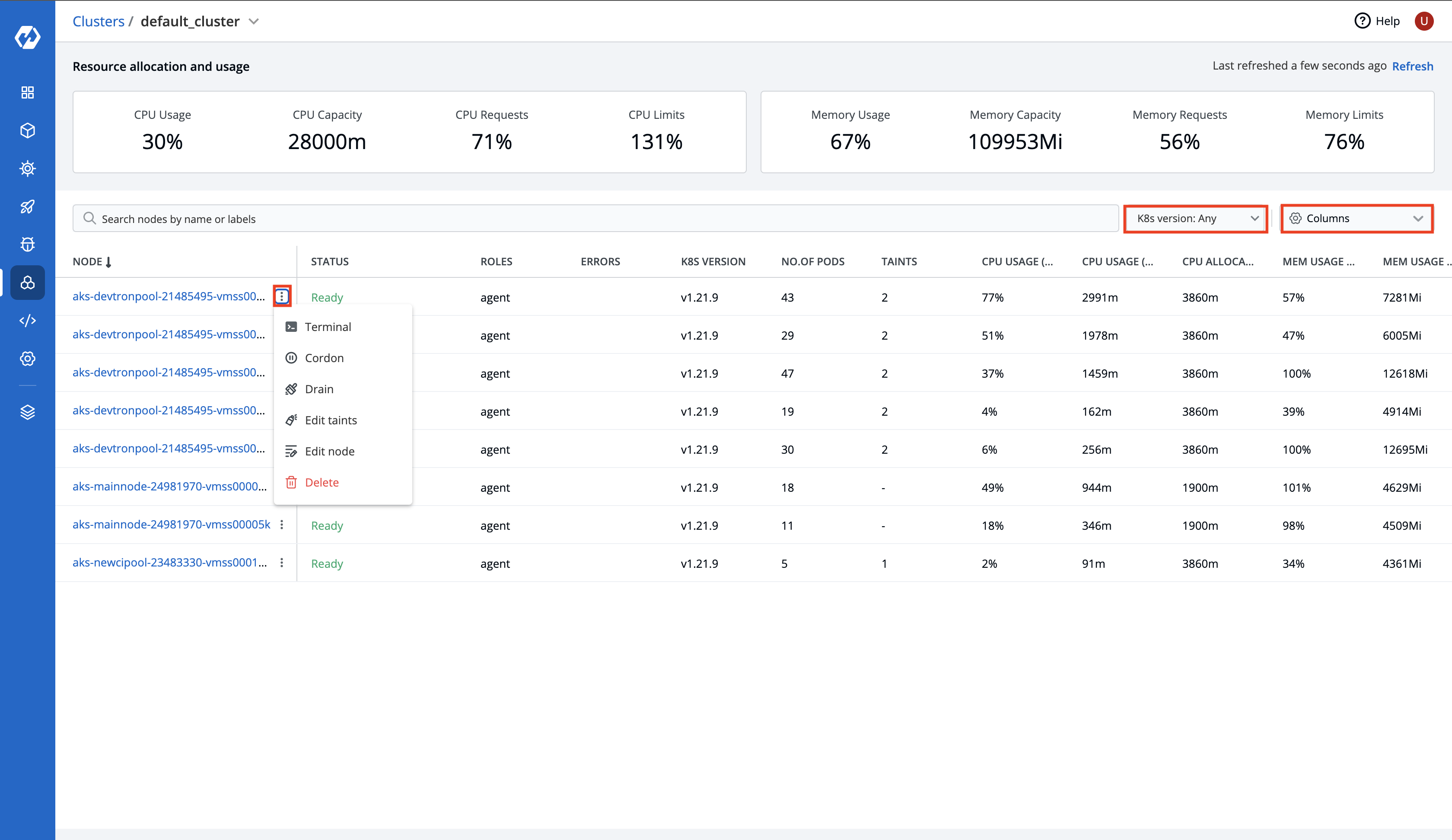
+## Nodes
+
+You can see the list of nodes available in your cluster. Typically you have several nodes in a cluster; in a learning or resource-limited environment, you might have only one node.
+
+The components on a typical node include the `kubelet`, a `container runtime`, and the `kube-proxy`.
+
+
+
+If you have multiple nodes, you can search a node by name or label in the search bar.
+
+| Fields | Description |
+| --- | --- |
+| **Node** | User-defined name for the node in Devtron. E.g. `demo-new`.
Note: Two nodes cannot have the same name at the same time. |
+| **Status** | Status of a node. It can be either `Ready` or `Not Ready`. |
+| **Roles** | Shows the roles of a node. |
+| **Errors** | Shows the error in nodes. |
+| **K8s Version** | Shows the version of Kubernetes cluster. |
+| **No. of Pods** | Shows the number of namespaces or pods in a node. |
+| **CPU Usage** | Shows the CPU consumption in a node. |
+| **Mem Usage** | Shows the memory consumption in a node |
+| **Age** | Shows the time that the pod has been running since the last restart. |
+
+To display a parameter of a node, use the `Columns` on the right side, select the parameter you want to display from the drop-down list and click `Apply`.
+
+## Manage Nodes
+
+Your applications run on pods, and pods run on Nodes. But sometimes, Kubernetes scheduler cannot deploy a pod on a Node for several reasons. As an example, node is not ready, node is not reachable, network is unavailable etc.
+
+Using the Devtron UI, you will be able to:
+* [Debug a node](#debug-a-node)
+* [Cordon a node](#cordon-a-node)
+* [Drain a node](#drain-a-node)
+* [Taint a node](#taint-node)
+* [Edit a node](#edit-a-node)
+* [Delete a node](#delete-a-node)
+
+To see the summary of a node, click the specific node.
+
+
+
+### Debug a Node
+
+You can debug a node via Terminal by selecting your namespace and image from the list that has all CLI utilities like kubectl, helm, netshoot etc. or can use a custom image, which is publicly available.
+
+
+
+* Go to the `Clusters` section from the left navigation pane.
+* Select your cluster.
+* Search a node by name or label in the search bar.
+* On the node, click the ellipsis button and then click `Terminal`.
+* Debug a node by selecting the terminal shell `bash` or `sh`.
+
+
+### Cordon a Node
+
+Cordoning a node means making the node unschedulable. After cordoning a node, new Pods cannot be scheduled on this node.
+
+
+
+* On the node, click the ellipsis button and then click `Cordon`.
+* A dialog box with message `Cordoning this node will mark this node as unschedulable. By cordoning a node, you can be sure that no new pods will be scheduled on this node` is displayed.
+* The status of the node shows `SchedulingDisabled` with `Unschedulable` parameter set as `true`.
+
+Similarly, you can uncordon a node by clicking `Uncordon`. After a node is uncordoned, new Pods can be scheduled on the node.
+
+### Drain a Node
+
+Before performing maintenance on a node, draining a node evicts all of your pods safely from a node. Safe evictions allow the pod’s containers to gracefully terminate and honour the `PodDisruptionBudgets` you have specified (if relevant).
+
+After the node is drained, all Pods (including those managed by DaemonSets) in the node will be automatically drained to other nodes in the cluster, and the drained node will be set to cordoned status.
+
+
+
+* On the node, click the ellipsis button and then click `Drain`.
+* A dialog box with message `Drain will cordon off the node and evict all pods of the node` is displayed.
+* Click `Drain Node`.
+
+You can also select from the following conditions before draining a node:
+
+| Name | Usage |
+| --- | --- |
+| **Grace Period** | Period of time in seconds given to each pod to terminate gracefully. If negative, the default value specified in the pod will be used. |
+| **Delete empty directory data** | Enabling this field will delete the pods using empty directory data when the node is drained. |
+| **Disable eviction (use with caution** | Enabling this field will force drain to use delete, even if eviction is supported. This will bypass checking `PodDisruptionBudgets`.
Note: Make sure to use with caution. |
+| **Force drain** | Enabling this field will force drain a node even if there are pods that do not declare a controller. |
+| **Ignore DaemonSets** | Enabling this field will ignore DaemonSet-managed pods. |
+
+### Taint a Node
+
+Taints are `key:value` pairs associated with effect. After you add taints to nodes, you can set tolerations on a pod to allow the pod to be scheduled to nodes with certain taints. When you taint a node, it will repel all the pods except those that have a toleration for that taint. A node can have one or many taints associated with it.
+
+**Note**: Make sure to check taint validations before you add a taint.
+
+
+
+* On the node, click the ellipsis button and then click `Edit taints`.
+* Click `Add taint`.
+* On the `Key` and `Value` fields, enter the `key:value` pairs and select the [taint effect](#taint-effects) from the drop-down list.
+* Click `Save`.
+* You can also delete the added taint by clicking delete button.
+
+#### Taint Effects
+
+A taint can produce three possible effects:
+
+| Effect | Description |
+| --- | --- |
+| **NoSchedule** | The Kubernetes scheduler will only allow scheduling pods that have tolerations for the tainted nodes. |
+| **PreferNoSchedule** | The Kubernetes scheduler will try to avoid scheduling pods that do not have tolerations for the tainted nodes. |
+| **NoExecute** | Kubernetes will evict the running pods from the nodes if the pods do not have tolerations for the tainted nodes. |
+
+### Edit a Node
+
+`Edit node` allows you to directly edit any node. It will open the editor which contains all the configuration settings in which the default format is YAML. You can edit multiple objects, although changes are applied one at a time.
+
+
+
+* You can edit or modify the parameters or values of a node by clicking `Edit node`.
+* Click `Review Changes` to compare the changes in the YAML file.
+* Click `Update Node`.
+
+
+### Delete a Node
+
+* Search a node by name or label in the search bar.
+* On the node, click the ellipsis button and then click `Delete`.
+
+The node will be deleted from the cluster.
+
+
+## Access Cluster via Terminal for Troubleshooting
+
+User with [Super admins](https://docs.devtron.ai/global-configurations/authorization/user-access#assign-super-admin-permissions) access can now troubleshoot cluster issues by accessing the cluster terminal from Devtron. You can select an image from the list that has all CLI utilities like kubectl, helm, netshoot etc. or can use a custom image, which is publicly available.
+
+To troubleshoot a cluster or a specific node in a cluster, click the terminal symbol on the right side.
+
+
+
+* You will see the user-defined name for the cluster in Devtron. E.g. `default-cluster`.
+* In the `Nodes` field, select the node from the drop-down list you want to troubleshoot. E.g. `demo-new`.
+* Select the namespace from the drop-down list which you have added in the [Environment](https://docs.devtron.ai/global-configurations/cluster-and-environments#add-environment) section.
+* Select the image from the drop-down list which includes all CLI utilities or you can use a custom image, which is publicly available.
+* Select the terminal shell from the drop-down list (e.g. `sh`, `bash`) to troubleshoot a node.
+
+
+### One of the Use Cases: Debug Pod
+
+You can also create pod for debugging which will connect to pod terminal. To find out why the particular pod is not running, you can check `Pod Events` and `Pod Manifest` for details.
+
+* Check the current state of the Pod and recent events with the following command:
+
+```bash
+kubectl get pods
+```
+
+* To know more information about each of these pods and to debug a pod depending on the state of the pods, run the following command:
+
+```bash
+kubectl describe pod
+```
+
+ * If the pod status shows `Pending`, it means that it cannot be scheduled onto a node. Generally this is because there are insufficient resources of one type or another that prevent scheduling.
+ * If the pod is stuck in the `Waiting` state, then it has been scheduled to a worker node, but it cannot run on that machine. One of the most common reason of Waiting pods is a failure to pull the container image.
+ * If the pod status shows `CrashLoopBackOff`, it may because some of the containers inside a pod are not operating on the default access token when trying to interact with API.
+
+
+Here, you can see configuration information about the container(s) and Pod (labels, resource requirements, etc.), as well as status information about the container(s) and Pod (state, readiness, restart count, events, etc.).
+
+
+ **Note**: A container can have no or multiple shells running in it. If you are not able to create a successfull connection, try changing the shell, as the container may not have that shell running.
+
+
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/README.md b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/README.md
index 1ec31a6ec8..ee4810afca 100644
--- a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/README.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/README.md
@@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
-_**This documentaion consist of authorizations available in Devtron**_
+`Authorization` section describes how to authenticate and authorize access to resources, also managing role-based access levels in Devtron.
-**Parts of the documentaion**
+Access can be added to a user via:
-[User Permissions](user-access.md)
+* [User Permissions](user-access.md)
-[Permission Groups](permission-groups.md)
+* [Permission Groups](permission-groups.md)
-[API Tokens](api-tokens.md)
\ No newline at end of file
+* [API Tokens](api-tokens.md)
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/api-tokens.md b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/api-tokens.md
index b5607aa26e..52226b5df2 100644
--- a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/api-tokens.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/api-tokens.md
@@ -4,84 +4,85 @@ API tokens are the access tokens for authentication. Instead of using username a
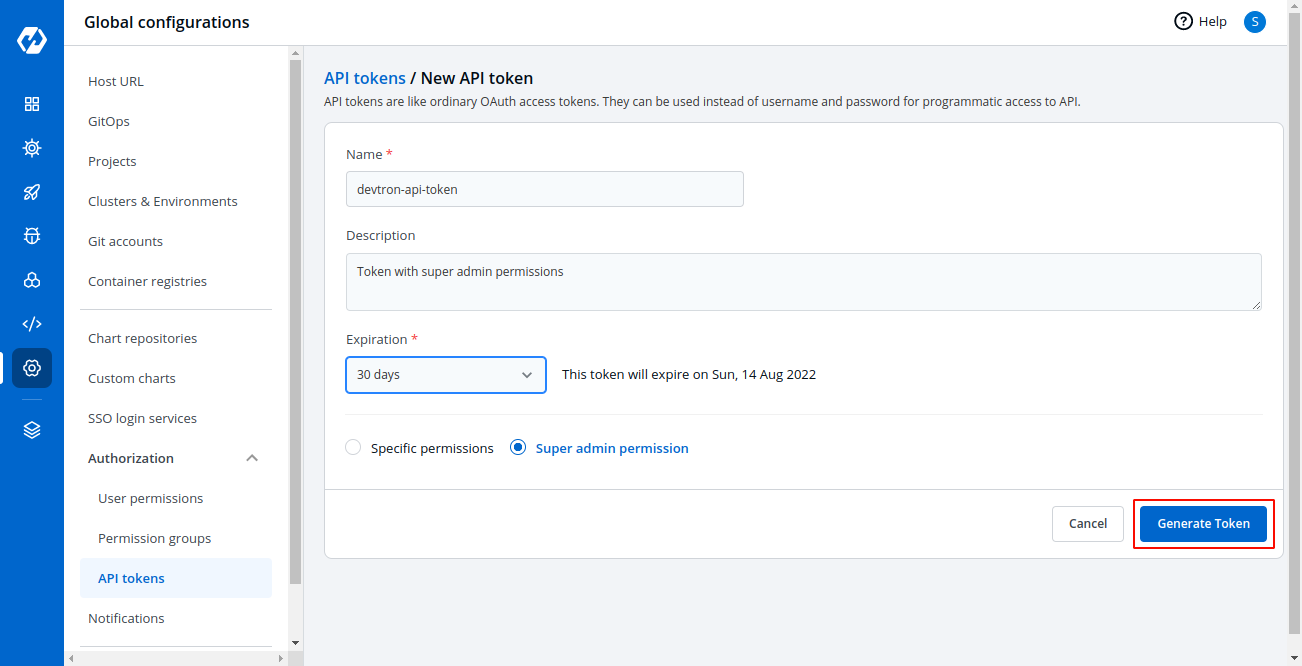
## Generate API Token
-To generate API tokens, go to Global Configurations -> Authorization -> API tokens and click `Generate New Token`.
+To generate API tokens, go to `Global Configurations -> Authorization -> API tokens` and click `Generate New Token`.

-1. Enter a name for the token.
-2. Add Description.
+* Enter a name for the token.
+* Add Description.
+* Select an expiration date for the token (7 days, 30 days, 60 days, 90 days, custom and no expiration).
-3. Select an Expiration date for the token (7 days, 30 days, 60 days, 90 days, custom and no expiration).

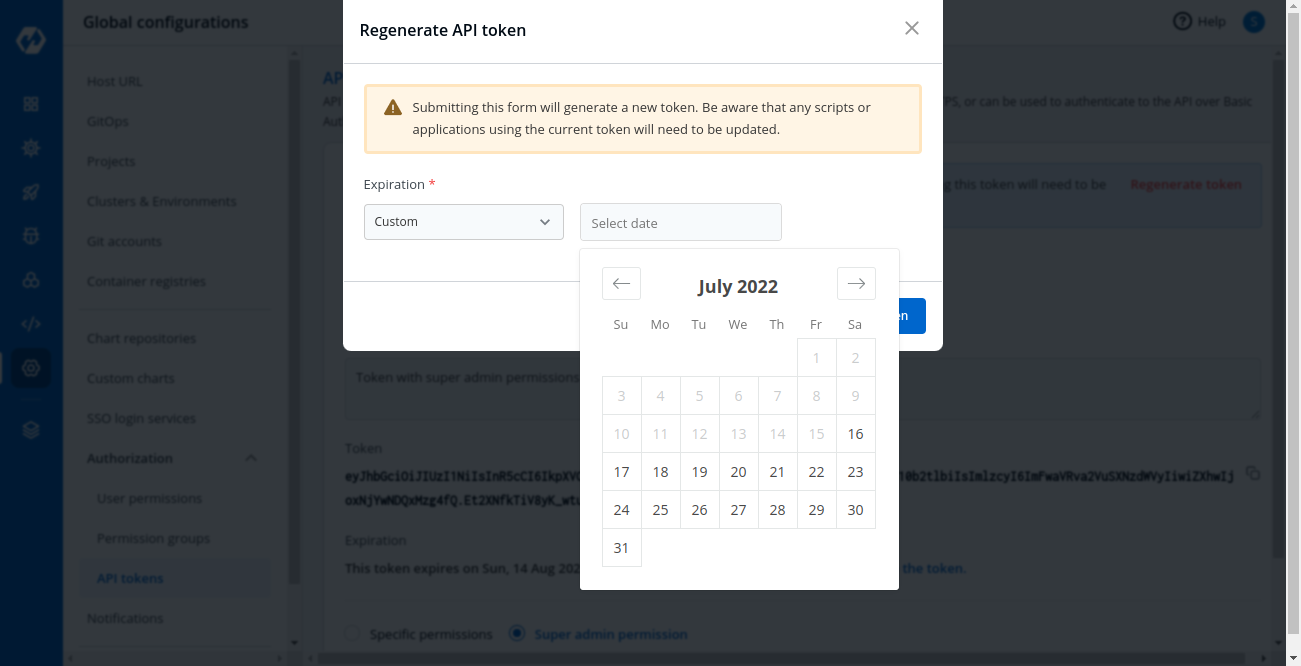
-To select a custom expiration date, select `Custom` from the drop-down. This will pop-up a calender from where you can select your custom expiration date for the API token.
+* To select a custom expiration date, select `Custom` from the drop-down list. In the adjacent field, you can select your custom expiration date for the API token.
-
+
-4. Assign permissions to the token. To generate a token with super admin permission, select super admin permission.
-
+* You can assign permission to the token either with:
-Or select specific permission if you want to generate a token with a specific role over a particular Devtron app or Helm app or chart group.
+ * **Super admin permission**: To generate a token with super admin permission, select `Super admin permission`.
-
+ * **Specific permissions**: Selecting `Specific permissions` option allows you to generate a token with a specific role for:
-5. Now click on Generate Token.
+
+
-A pop-up window will appear over the screen from where you can copy the API token.
+* Click `Generate Token`.
-
+A pop-up window will appear on the screen from where you can copy the API token.
+
## Use API Token
-Once devtron api token has been generated, you can use this token to hit devtron apis using any api testing tool like Jmeter, postman, citrus. Using postman here.
+Once Devtron API token has been generated, you can use this token to request Devtron APIs using any API testing tool like Jmeter, Postman, Citrus. Using Postman here as an example.
-Open postman. Enter the request URL with POST method and under HEADERS, enter the API token as shown in the image below.
+Open Postman. Enter the request URL with `POST` method and under HEADERS, enter the API token as shown in the image below.

-Now, under body, provide the api payload as shown below and click on Send.
+In the `Body` section, provide the API payload as shown below and click `Send`.

-As soon as you click on send, the create application api will be triggered and a new devtron app will be created as you mentioned in the payload.
+As soon as you click `Send`, the created application API will be triggered and a new Devtron app will be created as provided in the payload.

## Update API Token
-To set a new expiration date or to make changes in permissions assigned to the token, we need to update the API token.
-To update the API token, click over the token name or click on the edit icon.
+To set a new expiration date or to make changes in permissions assigned to the token, we need to update the API token in Devtron.
+To update the API token, click the token name or click on the edit icon.

-To set a new expiration date, you can regenerate the API token. Any scripts or applications using this token will need to be updated. To regenerate a token, click on regenerate token. A pop-up window will appear on the screen from where you can select a new expiration date and then click on `regenerate token`.
+To set a new expiration date, you can regenerate the API token. Any scripts or applications using this token must be updated. To regenerate a token, click `Regenerate token`.
+
+A pop-up window will appear on the screen from where you can select a new expiration date.

-Select a new expiration date and click on regenerated token.
+Select a new expiration date and click `Regenerate token`.

-This will generated a new token with a new expiration date.
+This will generate a new token with a new expiration date.
-
-To update API token permissions, give the permissions as you want to and click on update token.
+To update API token permissions, give the permissions as you want to and click `Update Token`.

-
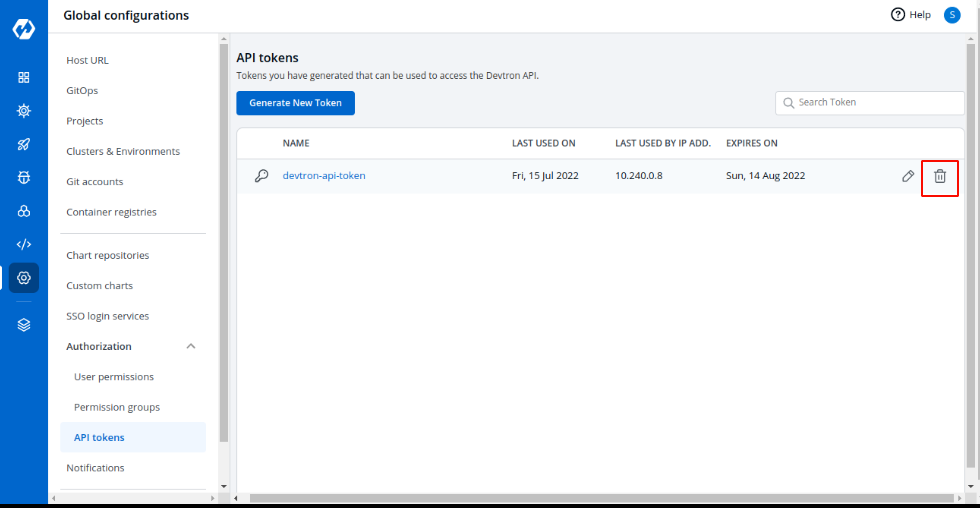
## Delete API Token
To delete an API token, click `delete` icon. Any applications or scripts using this token will no longer be able to access the Devtron API.
-
+
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/permission-groups.md b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/permission-groups.md
index 944cd77e6e..7e3d4c5f77 100644
--- a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/permission-groups.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/permission-groups.md
@@ -1,15 +1,14 @@
# Permission Groups
-This is used to assign user to a particular group and user inherits all the permissions granted to this group. The `Permission groups` section contains a drop-down of all existing groups on which you have access. This is optional field and more than one groups can be selected for a user.
+Using the `Permission groups`, you can assign a user to a particular group and a user inherits all the permissions granted to the group.
+The advantage of the `Permission groups` is to define a set of privileges like create, edit, or delete for the given set of resources that can be shared among the users within the group.
-The advantage of the groups is to define a set of privileges like create, edit, or delete for the given set of resources that can be shared among the users within the group. Users can be added to an existing group to utilize the privileges that it grants. Any access change to group is reflected immediately in user access.
+**Note**: The [User permissions](https://docs.devtron.ai/global-configurations/authorization/user-access) section for `Specific permissions` contains a drop-down list of all existing groups for which a user has an access. This is an optional field and more than one groups can be selected for a user.
-You can select the group which you are creating in the `Group permissions` section inside `Add users`.
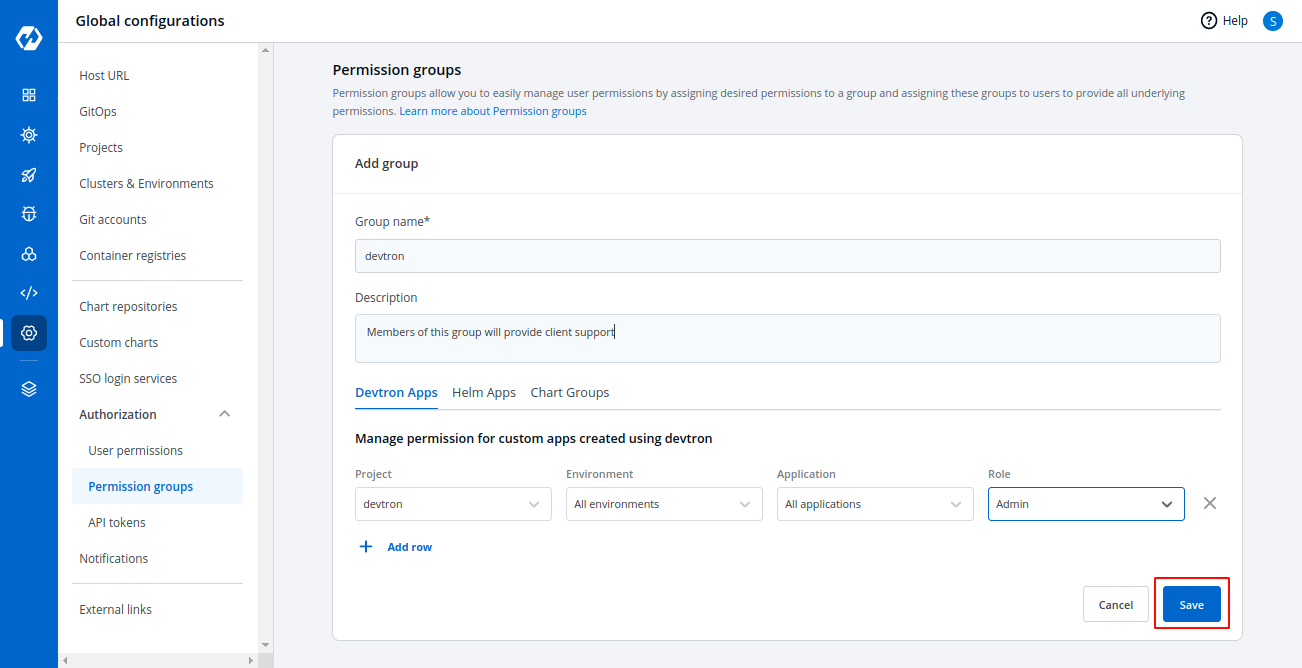
+## Add Group
-## 1. Add new Group
-
-Go to `Global configurations` -> `Authorization` -> `Permission group` and click on `Add Group` to create a new group.
+To add a group, go to the `Authorization > Permissions groups` section of `Global Configurations`. Click **Add group**.

@@ -17,32 +16,114 @@ Enter the `Group Name` and `Description`.

-## 2. Create permission Group
+Assign the permissions of groups to users to manage access for:
+
+ * [Devtron Apps](#devtron-apps-permissions)
+ * [Helm Apps](#helm-apps-permissions)
+ * [Kubernetes Resources](#kubernetes-resources-permissions)
+ * [Chart Groups](#chart-group-permissions)
+
+### Devtron Apps Permissions
+
+In `Devtron Apps` option, you can provide access to a group to manage permission for custom apps created using Devtron.
+
+**Note**: The `Devtron Apps` option will be available only if you install [CI/CD integration](https://docs.devtron.ai/usage/integrations/build-and-deploy-ci-cd).
+
+Provide the information in the following fields:
+
+
+
+
+| Registry Type | Credentials |
+| --- | --- |
+| **Project** | Select a project from the drop-down list to which you want to give permission to the group. You can select only one project at a time.
Note: If you want to select more than one project, then click `Add row`. |
+| **Environment** | Select the specific environment or all environments from the drop-down list.
Note: If you select `All environments` option, then a user gets access to all the current environments including any new environment which gets associated with the application later. |
+| **Application** | Select the specific applications or all applications from the drop-down list corresponding to your selected Environments.
Note: If you select `All applications` option, then a user gets access to all the current applications including any new application which gets associated with the project later. |
+| **Role** | Select one of the [roles](#role-based-access-levels) to which you want to give permission to the user: |
+
+You can add multiple rows for `Devtron Apps` permission.
+
+Once you have finished assigning the appropriate permissions for the groups, Click `Save`.
+
+### Helm Apps Permissions
+
+In `Helm Apps` option, you can provide access to a group to manage permission for Helm apps deployed from Devtron or outside Devtron.
+
+Provide the information in the following fields:
+
+
+
+| Registry Type | Credentials |
+| --- | --- |
+| **Project** | Select a project from the drop-down list to which you want to give permission to the group. You can select only one project at a time.
Note: If you want to select more than one project, then click `Add row`. |
+| **Environment or cluster/namespace** | Select the specific environment or `all existing environments in default cluster` from the drop-down list.
Note: If you select `all existing + future environments in default cluster` option, then a user gets access to all the current environments including any new environment which gets associated with the application later. |
+| **Application** | Select the specific application or all applications from the drop-down list corresponding to your selected Environments.
Note: If `All applications` option is selected, then a user gets access to all the current applications including any new application which gets associated with the project later. |
+| **Role** | Select one of the [roles](#role-based-access-levels) to which you want to give permission to the user: |
+
+You can add multiple rows for Devtron app permission.
+
+Once you have finished assigning the appropriate permissions for the groups, Click `Save`.
+
+
+### Kubernetes Resources Permissions
+
+In `Kubernetes Resources` option, you can provide permission to view, inspect, manage, and delete resources in your clusters from [Kubernetes Resource Browser](https://docs.devtron.ai/usage/deploy-resource-browser) page in Devtron. You can also create resources from the Kubernetes Resource Browser page.
+
+**Note**: Only super admin users will be able to see `Kubernetes Resources` tab and provide permission to other users to access `Resource Browser`.
+
+To provide Kubernetes resource permission, click `Add permission`.
+
+
+
+On the `Kubernetes resource permission`, provide the information in the following fields:
+
+
+
+
+| Registry Type | Credentials |
+| --- | --- |
+| **Cluster** | Select a cluster from the drop-down list to which you want to give permission to the user. You can select only one cluster at a time.
Note: To add another cluster, then click `Add another`. |
+| **Namespace** | Select the namespace from the drop-down list. |
+| **API Group** | Select the specific API group or `All API groups` from the drop-down list corresponding to the K8s resource. |
+ **Kind** | Select the kind or `All kind` from the drop-down list corresponding to the K8s resource. |
+ **Resource name** | Select the resource name or `All resources` from the drop-down list to which you want to give permission to the user. |
+| **Role** | Select one of the [roles](#role-based-access-levels) to which you want to give permission to the user and click `Done`: |
+
+You can add multiple rows for Kubernetes resource permission.
+
+Once you have finished assigning the appropriate permissions for the groups, Click `Save`.
+
+### Chart Group Permissions
+
+In `Chart group permission` option, you can manage the access of groups for Chart Groups in your project.
+
+**Note**: The `Chart group permission` option will be available only if you install [CI/CD integration](https://docs.devtron.ai/usage/integrations/build-and-deploy-ci-cd).
-Once you have given the group name and group description.
+
-Assign the permissions of groups in the `Devtron Apps`, `Helm Apps` or `Group Chart` permissions section. Manage the project, environment, application and role access the same as we discuss in the user permissions section.
+**NOTE:** You can only give users the ability to `create` or `edit`, not both.
-
+| Action | Permissions |
+| :--- | :--- |
+| View | Enable `View` to view chart groups only. |
+| Create | Enable `Create` if you want the users to create, view, edit or delete the chart groups. |
+| Edit | - **Deny**: Select `Deny` option from the drop-down list to restrict the users to edit the chart groups.
- **Specific chart groups**: Select the `Specific Charts Groups` option from the drop-down list and then select the chart group for which you want to allow users to edit.
|
-You can add multiple rows for the `Devtron Apps` and `Helm Apps` Permissions section.
+Click `Save`once you have configured all the required permissions for the groups.
-Once you have finished assigning the appropriate permissions for the permission group, click on `Save`.
-## 3. Edit Group Permissions
+### Edit Permissions Groups
-You can edit the permission groups by clicking on the `downward arrow.`
+You can edit the permission groups by clicking the `downward arrow.`

-Then you can edit the permission group here.
+Edit the permission group.

-Once you are done editing the permission group, click on `Save`.
+Once you are done editing the permission group, click `Save`.
-If you want to delete the groups with particular permission group, click on `Delete`.
+If you want to delete the groups with particular permission group, click `Delete`.
-## 4. Manage Chart Group Permissions
-The chart group permissions for the permission groups will be managed in the same way as for the users. For reference, check Manage chart group permissions for users.
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/user-access.md b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/user-access.md
index b19da4f0a6..d7429c2044 100644
--- a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/user-access.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/user-access.md
@@ -1,23 +1,23 @@
-# User Access
+# User Permissions
{% embed url="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VTqBRIFbuSU" caption="" %}
-Like any enterprise product, Devtron supports fine grained access control to the resources based on
+Like any enterprise product, Devtron supports fine grained access control to the resources based on:
-1. Type of action allowed on the Devtron resources (Create Vs View)
+1. Type of action allowed on Devtron resources (Create Vs View)
2. Sensitivity of the data (Editing image Vs Editing memory)
-Access can be added to the User either directly or via Groups.
+Access can be added to the User either directly or via [Permission groups](https://docs.devtron.ai/global-configurations/authorization/permission-groups).
## Role-based Access Levels
-Devtron supports 5 levels of access:
+Devtron supports the following levels of access:
-1. **View**: User with `view` only access has the least privilege. This user can only view combination of environments, applications and helm charts on which access has been granted to the user. This user cannot view sensitive data like secrets used in applications or charts.
-2. **Build and Deploy**: In addition to `view` privilege mentioned in above, user with `build and deploy` permission can build and deploy the image of permitted applications and helm charts to permitted environments.
-3. **Admin**: User with `admin` access can create, edit, delete and view permitted applications in permitted projects.
-4. **Manager**: User with `manager` access can do everything that an `admin` type user can do, in addition they can also give and revoke access of users for the applications and environments of which they are `manager`.
-5. **Super Admin**: User with `super admin` privilege has unrestricted access to all Devtron resources. Super admin can create, modify, delete and view any Devtron resource without any restriction; its like Superman without the weakness of Kryptonite. Super Admin can also add and delete user access across any Devtron resource, add delete git repository credentials, container registry credentials, cluster and environment.
+1. **View only**: User with `View only` access has the least privilege. This user can only view combination of environments, applications and helm charts on which access has been granted to the user. This user cannot view sensitive data like secrets used in applications or charts.
+2. **Build and Deploy**: In addition to `View only` access, user with `Build and deploy` permission can build and deploy the image of the permitted applications and helm charts to the permitted environments.
+3. **Admin**: User with `Admin` access can create, edit, delete and view permitted applications in the permitted projects.
+4. **Manager**: User with `Manager` access can do everything that an `Admin` type user can do, in addition, they can also give and revoke access of users for the applications and environments of which they are `Manager`.
+5. **Super Admin**: User with `Super admin` privilege has unrestricted access to all Devtron resources. Super admin can create, modify, delete and view any Devtron resource without any restriction; its like Superman without the weakness of Kryptonite. Super Admin can also add and delete user access across any Devtron resource, add delete git repository credentials, container registry credentials, cluster and environment.
## User Roles And Permissions
@@ -41,169 +41,161 @@ Devtron supports 5 levels of access:
| Manager | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Super Admin | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
-#### 3. User Access
+### 3. User Access
| User Roles | Add User Access | Edit User Access | Delete User Access |
| :--- | :---: | :---: | :---: |
| Manager | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Super Admin | Yes | Yes | Yes |
-#### 4. Global Configurations
+### 4. Global Configurations
| User Role | Add Global Config | Edit Global Config | Delete Global Config |
| :--- | :---: | :---: | :---: |
| Super Admin | Yes | Yes | Yes |
-To control the access of User and Group-
-Go to the left main panel -> `Select Global Configurations` -> Select `User Access`
+## Add User
-## Users
+To add a user, go to the `Authorization > User Permissions` section of `Global Configurations`. Click **Add user**.
-### 1. Add new user
+
-Click on `Add User`, to add one or multiple users.
+There are two types of permissions in Devtron:
-
+| Permission Type | Description |
+| --- | --- |
+| **Specific permissions** | Selecting [Specific permission](#assign-specific-permissions) option allows you to manage access and provide the [role-based access](#role-based-access-levels) accordingly for: |
+| **Super admin permission** | Selecting [Super admin permission](#assign-super-admin-permission) option will get full access to Devtron resources and the rest of the options will not be available. |
-### 2. Create User Permissions
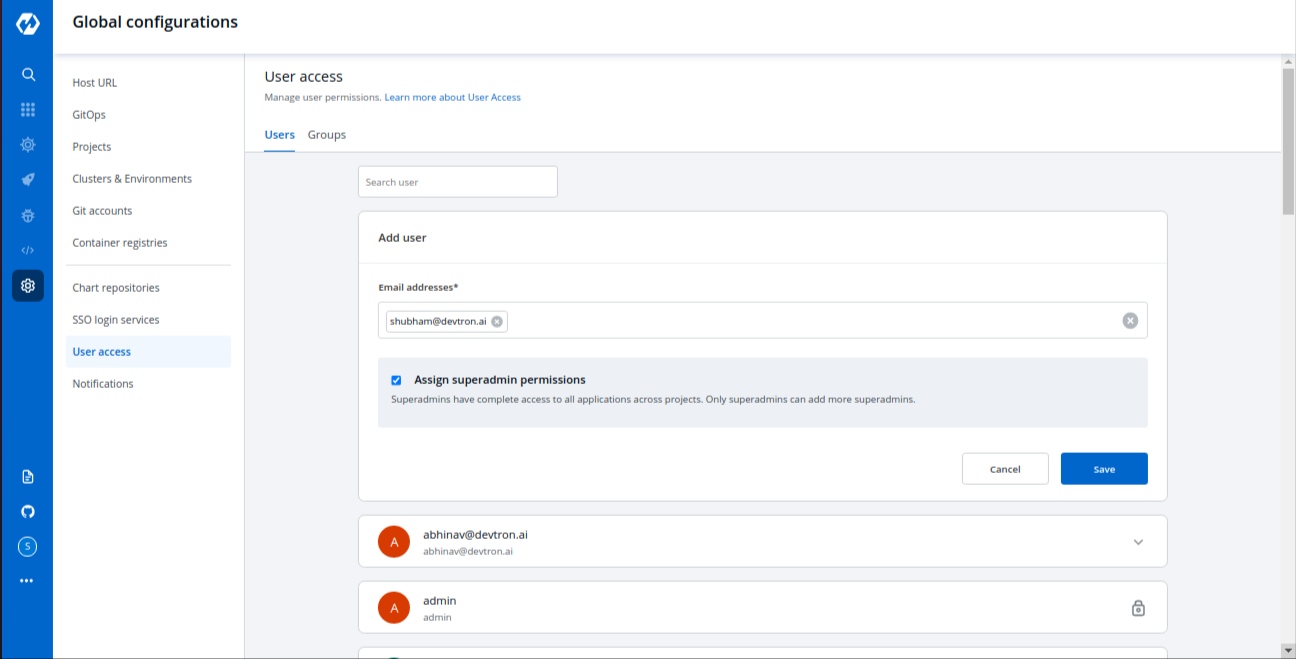
+### Assign Super admin permission
-When you click on Add User, you will see 6 options to set permission for users which are as follow:
+To assign a super admin access, go to the `Authorization > User Permissions` section of `Global Configurations`.
-- Email addresses
-- Assign super admin permissions
-- Group Permissions
-- Devtron Apps Permissions
- - Project
- - Environment
- - Applications
- - Roles
-- Helm Apps Permissions
- - Project
- - Environment or cluster/namespace
- - Applications
- - Permission
-- Chart group permissions
+
-## Email addresses:
+* Click **Add user**.
+* Provide the email address of a user. You can add more than one email address. Please note that email address must be same as that in the `email` field in the JWT token returned by OIDC provider.
+* Select `Super admin permission` and click `Save`.
+* A user now will have a [Super admin](#role-based-access-levels) access.
-In the `Email address` box, you have to provide the mail ID of the user to whom you want to give access to your applications.
+**Note**:
+* Only users with `Super admin permission` can assign super admin permissions to a user.
+* We suggest that super admin access must be given to the selected users only.
-**`IMP`** Please note that Email address should be same as that in the `email` field in the JWT token returned by OIDC provider.
-### Assign super admin permissions
+### Assign Specific permissions
-If you check the option `Assign super admin permissions`, the user will get full access to your system and the rest of the options will disappear. Please check [above](#access-levels) to see permission levels. Only users with super admin permissions can assign super admin permissions to a user.
+To assign a specific permission, go to the `Authorization > User Permissions` section of `Global Configurations`.
-
+* Click **Add user**.
+* Provide the email address of a user. You can add more than one email address. Please note that email address must be same as that in the `email` field in the JWT token returned by OIDC provider.
+* Select `Specific permissions`.
+* Select the group permission from the drop-down list, if required.
+* Selecting `Specific permission` option allows you to manage access and provide the [role-based access](#role-based-access-levels) accordingly for
-Click on `Save` and your user will be saved with super admin permissions.
+ * [Devtron Apps](#devtron-apps-permissions)
+ * [Helm Apps](#helm-apps-permissions)
+ * [Kubernetes Resources](#kubernetes-resources-permissions)
+ * [Chart Groups](#chart-group-permissions)
-We suggest that super admin privileges should be given to only select few.
-If you don’t want to assign super admin permissions then you have to provide the rest of the information.
+### Devtron Apps Permissions
+In `Devtron Apps` option, you can provide access to a user to manage permission for custom apps created using Devtron.
-### Devtron Apps permissions
+**Note**: The `Devtron Apps` option will be available only if you install [CI/CD integration](https://docs.devtron.ai/usage/integrations/build-and-deploy-ci-cd).
-Access to devtron applications can be given to user by attaching permission directly to his/her email id through the `Devtron Apps` section. This section has 4 options to manage the permissions of your users.
+Provide the information in the following fields:
-- **Project**
+
-Select a project from the drop-down to which you want to give permission to the users. You can select only one project at a time if you want to select more than one project then click `Add row`.
+| Registry Type | Credentials |
+| --- | --- |
+| **Project** | Select a project from the drop-down list to which you want to give permission to the user. You can select only one project at a time.
Note: If you want to select more than one project, then click `Add row`. |
+| **Environment** | Select the specific environment or all environments from the drop-down list.
Note: If you select `All environments` option, then a user gets access to all the current environments including any new environment which gets associated with the application later. |
+| **Application** | Select the specific applications or all applications from the drop-down list corresponding to your selected Environments.
Note: If you select `All applications` option, then a user gets access to all the current applications including any new application which gets associated with the project later. |
+| **Role** | Select one of the [roles](#role-based-access-levels) to which you want to give permission to the user: |
-- **Environment**
+You can add multiple rows for Devtron app permission.
-In the `Environment` section, you can select one or more than one or all environments at a time. Click on the environment section, you will see a drop-down of your environments and select any environment on which you want to give permission to the user.
-
-**`IMP`** If `all environments` option is selected then user gets access to all current environments and any new environment which gets associated with this application later.
-
-- **Applications**
-
-Similarly, you can select `Applications` from the drop-down corresponding to your selected Environments. In this section, you can also give permissions to one or more than one or to all applications at a time.
-
-**`IMP`** If `all applications` option is selected then user gets access to all current applications and any new application which gets associated with this project later.
-
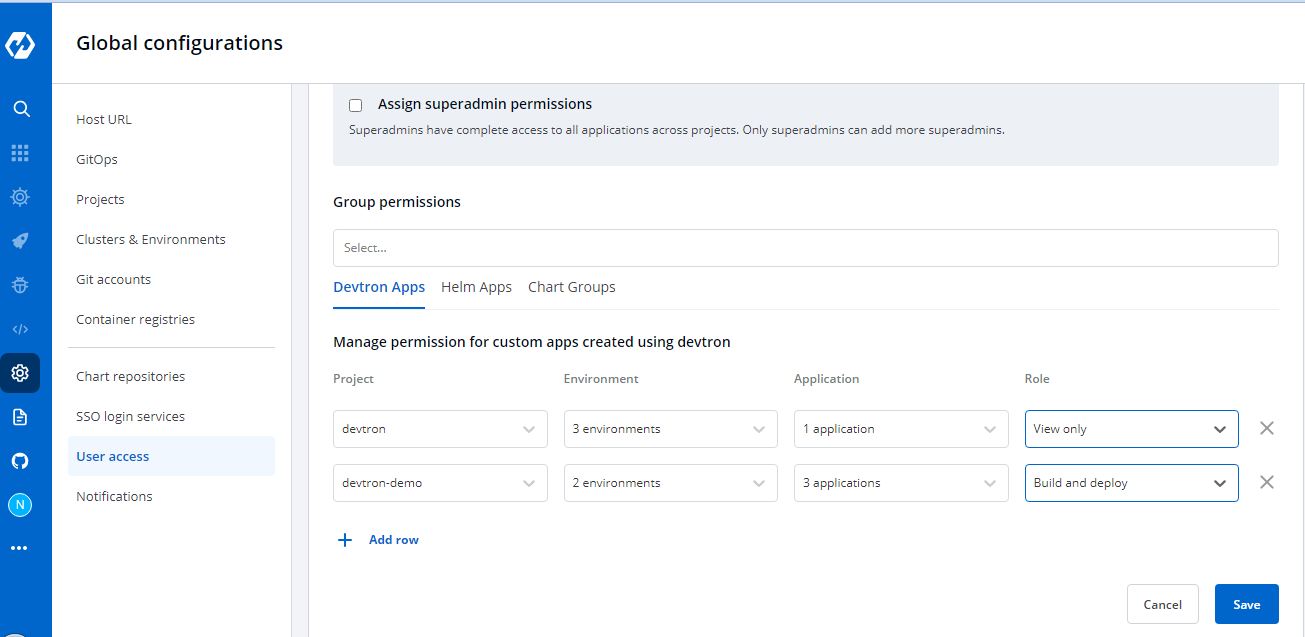
-- **Roles**
-
- Inside the `Role`, you actually choose which type of permissions you want to give to the users.
-
-There are four different view access levels/Role available for both User and Group as described [above](#access-levels):
-
-
-
-You can add multiple rows, for Devtron app permission.
-
-Once you have finished assigning the appropriate permissions for the listed users, Click on `Save`.
+Once you have finished assigning the appropriate permissions for the users, Click `Save`.
### Helm Apps Permissions
-Access to devtron applications can be given to user by attaching permission directly to his/her email id through the `Devtron Apps` section. This section has 4 options to manage the permissions of your users.
-
-- **Project**
+In `Helm Apps` option, you can provide access to a user to manage permission for Helm apps deployed from Devtron or outside Devtron.
-Select a project from the drop-down to which you want to give permission to the users. You can select only one project at a time if you want to select more than one project then click `Add row`.
+Provide the information in the following fields:
-- **Environment or cluster/namespace**
+
-In the `Environment` section, you can select one or more than one or all environments at a time. Click on the environment section, you will see a drop-down of your environments and select any environment on which you want to give permission to the user.
+| Registry Type | Credentials |
+| --- | --- |
+| **Project** | Select a project from the drop-down list to which you want to give permission to the user. You can select only one project at a time.
Note: If you want to select more than one project, then click `Add row`. |
+| **Environment or cluster/namespace** | Select the specific environment or `all existing environments in default cluster` from the drop-down list.
Note: If you select `all existing + future environments in default cluster` option, then a user gets access to all the current environments including any new environment which gets associated with the application later. |
+| **Application** | Select the specific application or all applications from the drop-down list corresponding to your selected Environments.
Note: If `All applications` option is selected, then a user gets access to all the current applications including any new application which gets associated with the project later. |
+| **Role** | Select one of the [roles](#role-based-access-levels) to which you want to give permission to the user: |
-**`IMP`** If `all environments` option is selected then user gets access to all current environments and any new environment which gets associated with this application later.
+You can add multiple rows for Devtron app permission.
-- **Applications**
+Once you have finished assigning the appropriate permissions for the users, Click `Save`.
-Similarly, you can select `Applications` from the drop-down corresponding to your selected Environments. In this section, you can also give permissions to one or more than one or to all applications at a time.
-**`IMP`** If `all applications` option is selected then user gets access to all current applications and any new application which gets associated with this project later.
+### Kubernetes Resources Permissions
-- **Permission**
+In `Kubernetes Resources` option, you can provide permission to view, inspect, manage, and delete resources in your clusters from [Kubernetes Resource Browser](https://docs.devtron.ai/usage/deploy-resource-browser) page in Devtron. You can also create resources from the Kubernetes Resource Browser page.
- Inside the `Role`, you actually choose which type of permissions you want to give to the users.
+**Note**: Only super admin users will be able to see `Kubernetes Resources` tab and provide permission to other users to access `Resource Browser`.
-There are four different view access levels/Role available for both User and Group as described [above](#access-levels):
+To provide Kubernetes resource permission, click `Add permission`.
-
-
-### Chart Group Permissions
+
-You can also manage the access of users to Chart Groups in your project.
+On the `Kubernetes resource permission`, provide the information in the following fields:
-**NOTE:** You can only give users the ability to `create` or `edit`, not both.
-Click on the checkbox of `Create`, if you want the users to create, view, edit, or delete the chart groups.
+
-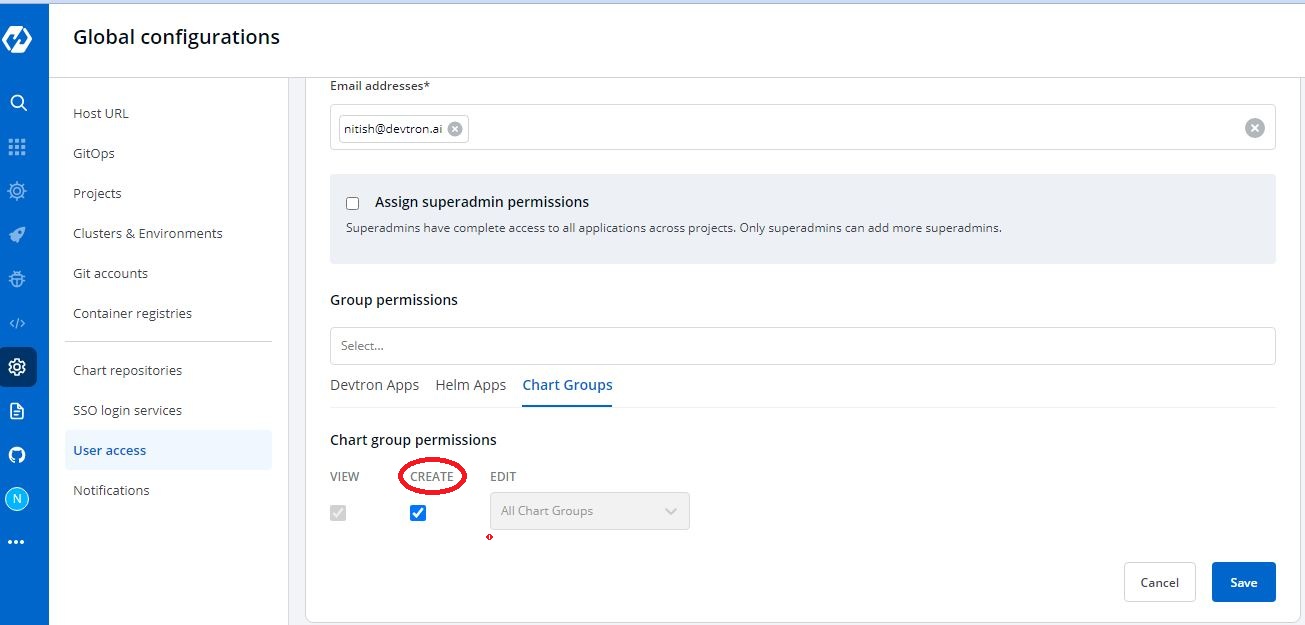
+| Registry Type | Credentials |
+| --- | --- |
+| **Cluster** | Select a cluster from the drop-down list to which you want to give permission to the user. You can select only one cluster at a time.
Note: To add another cluster, then click `Add another`. |
+| **Namespace** | Select the namespace from the drop-down list. |
+| **API Group** | Select the specific API group or `All API groups` from the drop-down list corresponding to the K8s resource. |
+ **Kind** | Select the kind or `All kind` from the drop-down list corresponding to the K8s resource. |
+ **Resource name** | Select the resource name or `All resources` from the drop-down list to which you want to give permission to the user. |
+| **Role** | Select one of the [roles](#role-based-access-levels) to which you want to give permission to the user and click `Done`: |
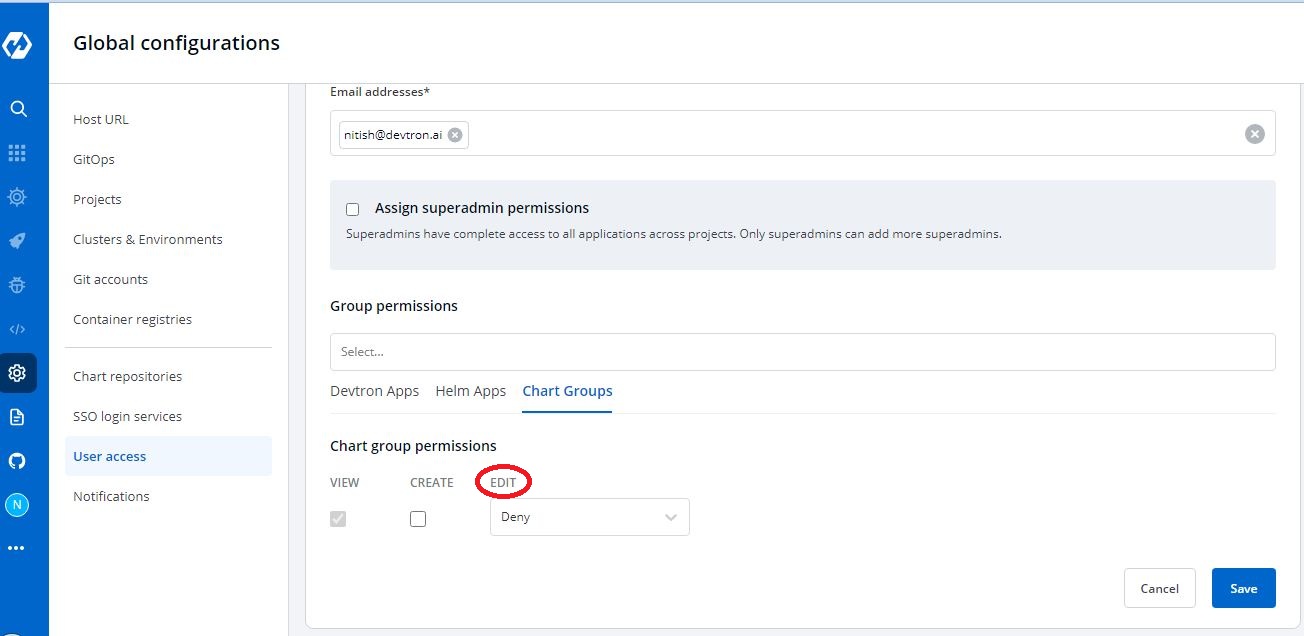
-To permit a user to only `edit` the chart groups, check `Specific chart group` from `Edit` drop-down. In the following field, select the chart group for which you want to grant the user edit permission.
+You can add multiple rows for Kubernetes resource permission.
-Go to `Edit` drop-down, if you want to `allow` or `deny` users to edit the chart groups.
+Once you have finished assigning the appropriate permissions for the users, Click `Save`.
-Select on `Deny` option from the drop-down, if you want to restrict the users to edit the chart groups.
+### Chart Group Permissions
-
+In `Chart group permission` option, you can manage the access of users for Chart Groups in your project.
-Select the `Specific Charts` option from the drop-down and then select the chart groups for which you want to allow users to edit, from the other drop-down menu.
+**Note**: The `Chart group permission` option will be available only if you install [CI/CD integration](https://docs.devtron.ai/usage/integrations/build-and-deploy-ci-cd).
-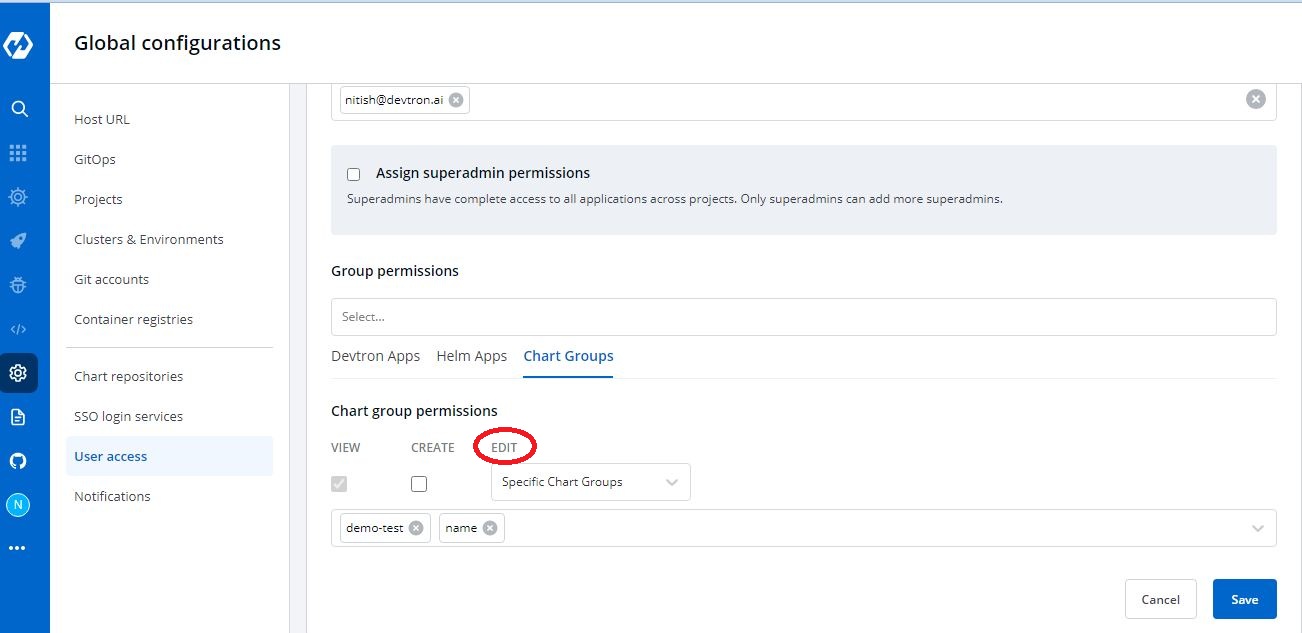
+
-Click on `Save`, once you have configured all the required permissions for the users.
+**NOTE:** You can only give users the ability to `create` or `edit`, not both.
| Action | Permissions |
| :--- | :--- |
-| View | Only can view chart groups |
-| Create | Can create, view, edit or delete |
-| Edit |
- **Deny:** Can't edit chart groups
- **Specific chart groups:** can edit specific chart group
|
+| View | Enable `View` to view chart groups only. |
+| Create | Enable `Create` if you want the users to create, view, edit or delete the chart groups. |
+| Edit | - **Deny**: Select `Deny` option from the drop-down list to restrict the users to edit the chart groups.
- **Specific chart groups**: Select the `Specific Charts Groups` option from the drop-down list and then select the chart group for which you want to allow users to edit.
|
+
+Click `Save`once you have configured all the required permissions for the users.
-### 3. Edit User Permissions
+### Edit User Permissions
-You can edit the user permissions, by clicking on the `downward arrow`.
+You can edit the user permissions by clicking on the `downward arrow`.

-Then you can edit the user permissions here.
+Edit the user permissions.
-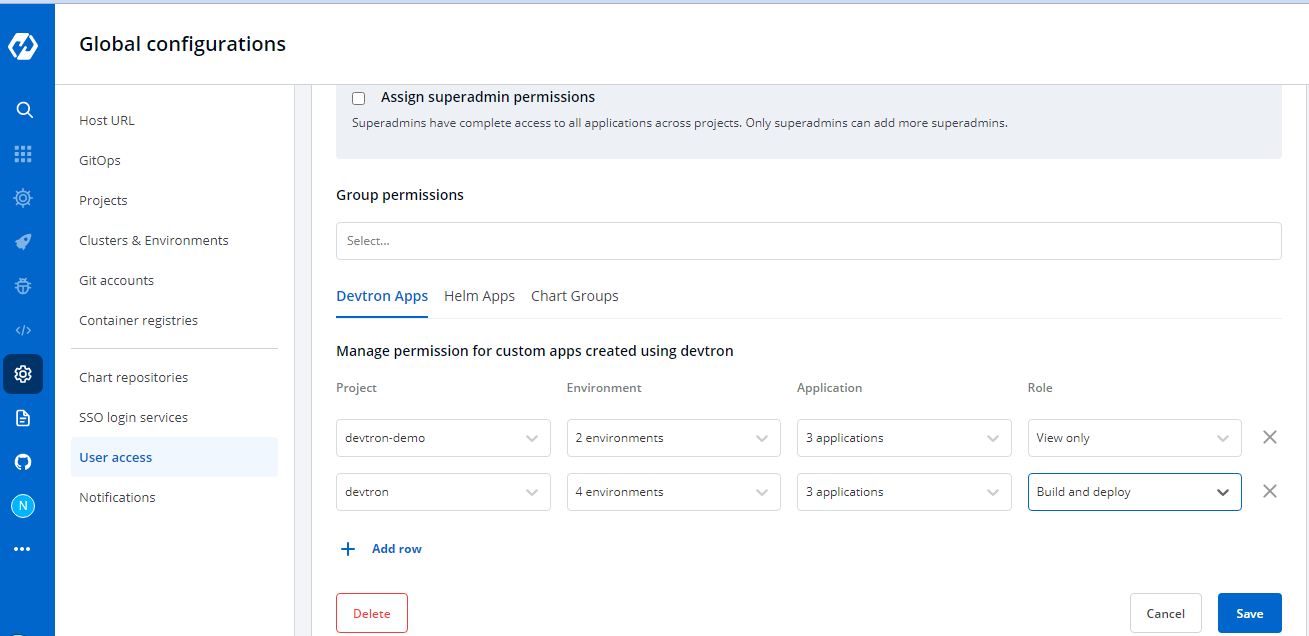
+After you have done editing the user permissions, click `Save`.
-After you have done editing the user permissions, click on `Save`.
+If you want to delete the user/users with particular permissions, click `Delete`.
-If you want to delete the user/users with particular permissions, click on `Delete`.
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/resource-browser.md b/docs/user-guide/resource-browser.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..48c2ff0140
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/user-guide/resource-browser.md
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
+# Resource Browser
+
+`Resource Browser` lists all of the resources running in your cluster. You can use it to view, inspect, manage, and delete resources in your cluster. You can also create resources from the `Resource Browser`.
+
+Resource Browser are helpful for troubleshooting issues. It supports multi-cluster.
+
+**Note**: To provide permission to a user to view, inspect, manage, and delete resources, go to the [Authorization > User Permissions](https://docs.devtron.ai/global-configurations/authorization/user-access) section of `Global Configurations`. You can also provide permission via [API token](https://docs.devtron.ai/global-configurations/authorization/api-tokens) or [Permission groups](https://docs.devtron.ai/global-configurations/authorization/permission-groups). Only super admin users will be able to see `Kubernetes Resources` tab and provide permission to other users to access `Resource Browser`.
+
+## Kubernetes Resources
+
+
+
+The following resources are grouped in the categories:
+
+* **Workloads** displays workloads (Cronjob, Deployment, StatefulSet, DaemonSet, Job, and Pod resources) deployed to clusters in your current project. Includes each workload's name, status, type, number of running and total desired Pods, namespace, and cluster.
+
+* **Config & Storage** display ConfigMap, Secret, PersistantVolume, PersistentVolumeClaim, Pod DisruptionBudget, resources which are used by applications for storing data. The configMap and secret data are provided as local ephemeral storage, which means there is no long-term guarantee about durability. A PersistentVolume (PV) is a piece of storage in the cluster that has been provisioned by server/storage/cluster administrator or dynamically provisioned using Storage Classes. It is a resource in the cluster just like node. Whereas, A PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC) is a request for storage by a user which can be attained from PV. It is similar to a Pod. Pods consume node resources and PVCs consume PV resources.
+
+
+* **Networking** displays your project's [Enpoints](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/endpoint-slices/), [NetworkPolicy](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/network-policies/) and [Service](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/) resources. Displays each resource's name, namespace, type, Cluster-IP, External-IP, Port(s), Age.
+
+* **RBAC** stands for Role-based access control which provides the authorization strategy for regulating access to cluster or resources based on the roles of individual users within your organization.
+
+* **Custom Resource** allows you to create your own API resources and define your own kind just like Pod, Deployment, ReplicaSet, etc.
+
+
+The following resources are grouped as uncategoried:
+
+** **Events** displays all the reports of an event in a cluster.
+
+** **Namespaces** displays the current list of namespaces in a cluster.
+
+### Search and Filter Resources
+
+You can search and filter resources by specific resource Kinds. You can also preview `Manifest`, `Events`, `Logs`, access `Terminal` by selecting ellipsis on the specific resource or `Delete` a specific resource.
+
+
+
+#### Manifest
+
+
+A manifest is a YAML file that describes each component or resource of your deployment and the state you want your cluster to be in once applied. Once you deploy, you can always edit your manifest file. A manifest specifies the desired state of an object that Kubernetes will maintain when you apply the manifest.
+
+#### Events
+
+An event is automatically generated in response to changes with other resources—like nodes, pods, or containers. For example, phases across a pod’s lifecycle transition from pending to running, or statuses like successful or failed may trigger a K8s event. The same goes for re-allocations and scheduling. These events are available until 15 minutes of deployment of the application.
+
+#### Logs
+
+Logs contain the logs of the Pods and Containers deployed which you can use for the process of debugging.
+
+
+### Create Kubernetes Resource
+
+**Note**: As a pre-requisite, you must have a basic understanding of Kubernetes Cluster, Resources, Kinds.
+
+You can create a Kubernetes resource by passing definition YAML file. You can create more than one resource by separating the resource YAMLs by ‘---’.
+
+An example that shows the required fields and object specifications for a Kubernetes Deployment:
+
+```bash
+apiVersion: apps/v1
+kind: Deployment
+metadata:
+ name: nginx-deployment
+ labels:
+ app: nginx
+spec:
+ replicas: 2
+ selector:
+ matchLabels:
+ app: nginx
+ template:
+ metadata:
+ labels:
+ app: nginx
+ spec:
+ containers:
+ - name: nginx
+ image: nginx:1.14.2
+ ports:
+ - containerPort: 80
+```
+
+* Click `Create` button on the upper right corner of the `Kubernetes Resource Browser` page.
+
+
+
+* Provide YAML containing K8s resource configuration and click `Apply`.
+
+
+
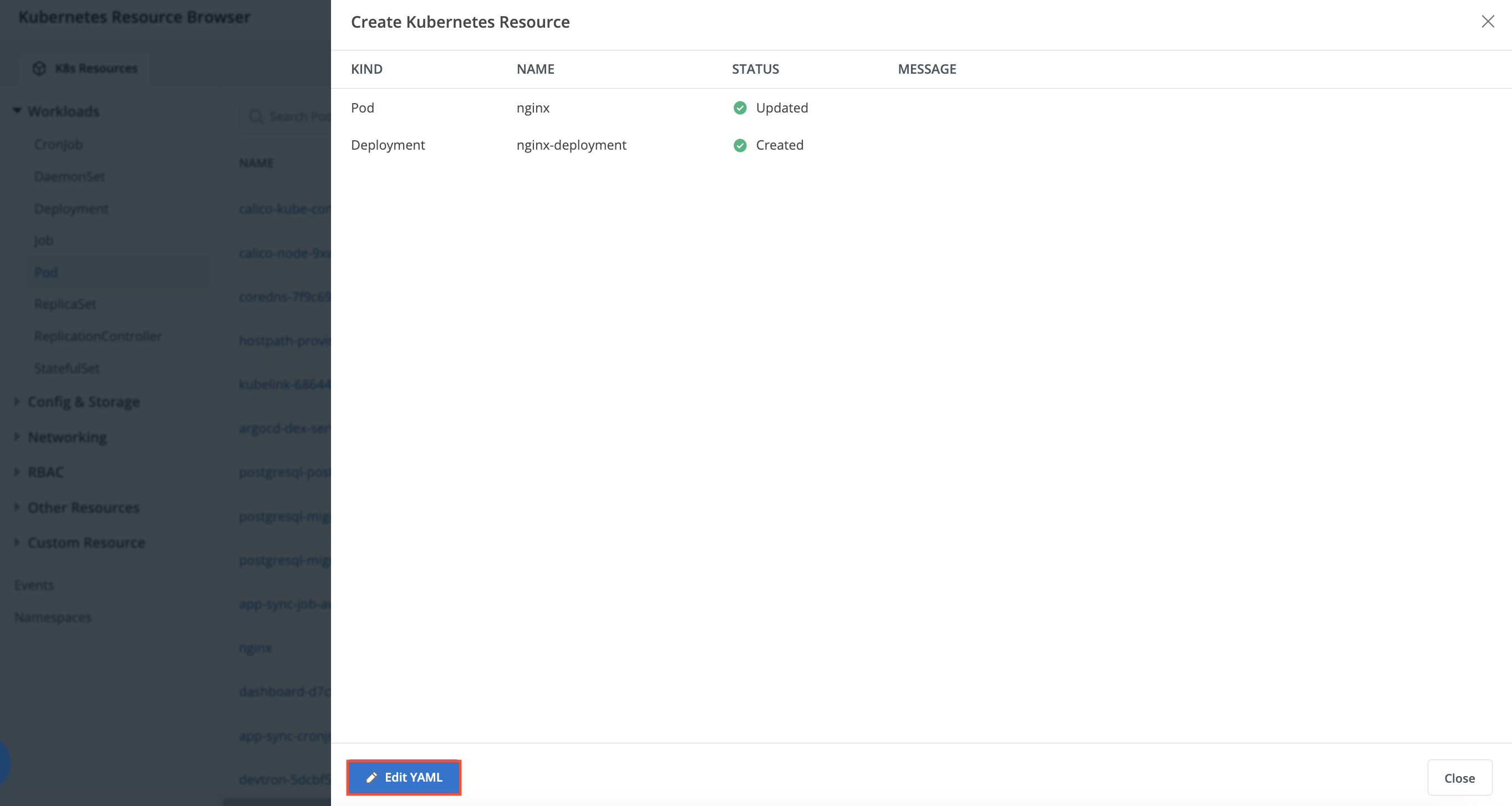
+* You will see the details of `Kind`, `Name`, `Status` and `Message` of the created resources.
+
+>Note: A message is displayed only when there is an error in the resource YAML.
+
+
+
+
+* If required, click `Edit YAML` to edit the YAML or click `Close`.
+
+* A new resource will be created or updated accordingly.
+
+
+
+
+